SQL Has 230 Keywords – With AI, These Are the Only Ones You Need to Know!
Will AI Replace SQL Knowledge?
Many believe that with AI tools, learning SQL is no longer necessary. The truth is different: SQL remains an essential skill for anyone working with data. Mastering the basics allows you to make the most of AI tools and solve problems in real time.
Imagine being in a meeting and your boss asks for a quick report… would you only rely on ChatGPT, or would you know how to write the query in seconds?
What is SQL?
SQL (Structured Query Language) was developed in the 1970s at IBM and became an ANSI and ISO standard in 1986.
It’s the most widely used language for querying, manipulating, and structuring data in relational databases.
Main Components of SQL
Before diving into examples, let’s review the key building blocks of SQL:
-
Queries: Instructions to retrieve data from the database.
-
Clauses: Parts of a query (e.g., SELECT, FROM, WHERE).
-
Predicates: Logical conditions that return true or false.
-
Expressions: Values or calculations used inside queries.
-
Statements: Complete blocks of code that perform an action.
-
White Space: Spaces, tabs, and line breaks that make code readable (ignored by SQL).
Creating Databases and Tables
Create a Database
Depending on the database engine, syntax may vary:
- MySQL: Allows character sets and collations.
CREATE DATABASE my_database_name
CHARACTER SET utf8mb4
COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;-
SQL Server: Often includes file specifications and configurations.
-
PostgreSQL: Offers flexible encoding and settings.
Create a Table
CREATE TABLE Customers (
CustomerID INT PRIMARY KEY,
FirstName VARCHAR(255),
LastName VARCHAR(255),
Age INT,
Email VARCHAR(255),
RegistrationDate DATE
);Basic SQL Queries
Select Data
SELECT CustomerID, FirstName, LastName
FROM Customers
WHERE City = 'London' AND Country = 'UK'
ORDER BY LastName ASC;SELECT: columns to retrieveFROM: source tableWHERE: filters resultsORDER BY: sorts results
Insert Data
INSERT INTO Customers (FirstName, LastName, Age, Email)
VALUES ('Ana', 'Lopez', 28, '[email protected]');Update Records
UPDATE Customers
SET Age = 29
WHERE CustomerID = 1;Delete Records
DELETE FROM Customers
WHERE CustomerID = 1;Beyond the Basics
Once you’ve mastered the essentials, explore advanced SQL concepts:
-
Joins: Combine data from multiple tables (INNER, LEFT, RIGHT, FULL, CROSS).
-
Subqueries: Queries nested inside other queries.
-
Aggregate Functions:
COUNT,SUM,AVG,MIN,MAXwithGROUP BY. -
Window Functions: Advanced calculations across related rows.
-
CTEs (Common Table Expressions): Temporary result sets for reuse.
-
Recursive Queries: Handle hierarchical data structures.
Recommended Resources
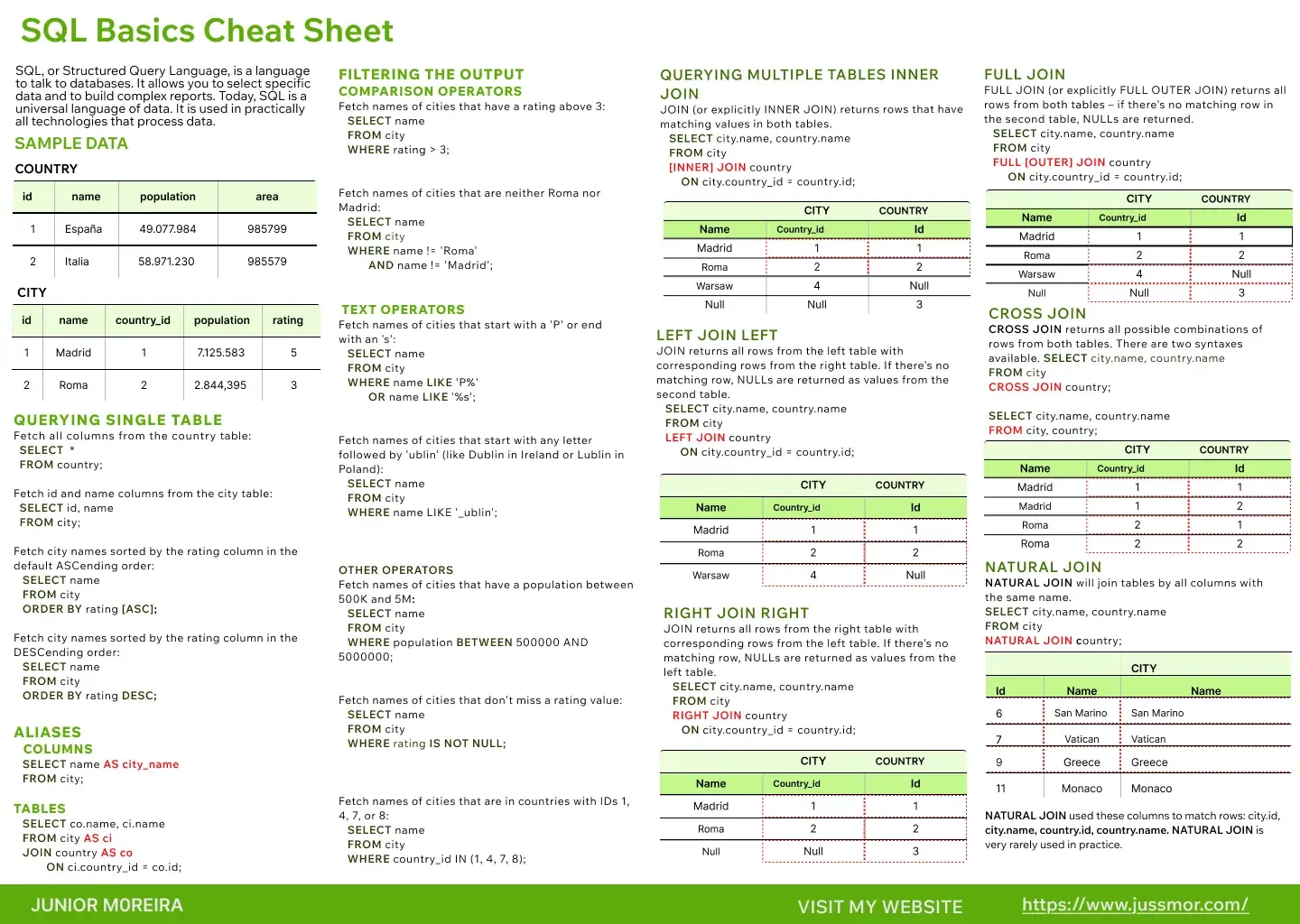
- 📄 Download my SQL Cheat Sheet (Download the Cheat Sheet HERE!)
- 📖 Learning SQL by Alan Beaulieu (great for beginners and advanced users).
Conclusion
SQL is far from obsolete — it’s still the universal language of data. By learning it, you’ll be able to:
-
Respond quickly to data requests at work.
-
Complement the power of AI tools.
-
Build a solid foundation for roles like analyst, engineer, or data scientist.
👉 What SQL topic are you most interested in? DM me if you have questions or visit my LinkendIn